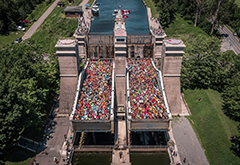1. Suez Canal:
The Panama Canal is an artificial 82 km (51 mi) waterway in Panama that connects the Atlantic Ocean with the Pacific Ocean. The canal cuts across the Isthmus of Panama and is a conduit for maritime trade. Canal locks are at each end to lift ships up to Gatun Lake, an artificial lake created to reduce the amount of excavation work required for the canal, 26 m (85 ft) above sea level, and then lower the ships at the other end. The original locks are 34 m (110 ft) wide. A third, wider lane of locks was constructed between September 2007 and May 2016. The expanded canal began commercial operation on June 26, 2016. The new locks allow transit of larger, post-Panamax ships, capable of handling more cargo. More details
3. Erie Canal:
4. Bridgewater Canal:
5. Peterborough Lift Lock:
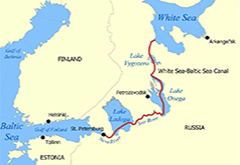
6. White Sea Baltic Canal:
7. British Canals History:
8. Canal du Midi:
10. Manchester Ship Canal:
The Grand Canal, known to the Chinese as the Beijing–Hangzhou Grand Canal, a UNESCO World Heritage Site, is the longest as well as one of the oldest canal or artificial river in the world and a famous tourist destination. Starting at Beijing, it passes through Tianjin and the provinces of Hebei, Shandong, Jiangsu and Zhejiang to the city of Hangzhou, linking the Yellow River and Yangtze River. The oldest parts of the canal date back to the 5th century BC, but the various sections were first connected during the Sui dynasty (581–618 AD). The Yuan and Ming dynasties significantly rebuilt the canal and altered its route to supply their capital Beijing. More details
12. Göta Canal:
The Göta Canal is a Swedish canal constructed in the early 19th century. It formed the backbone of a waterway stretching some 614 km (382 mi), linking a number of lakes and rivers to provide a route from Gothenburg (Göteborg) on the west coast to Söderköping on the Baltic Sea via the river Göta älv and the Trollhätte kanal, through the large lakes Vänern and Vättern. More details
The Göta Canal is a Swedish canal constructed in the early 19th century. It formed the backbone of a waterway stretching some 614 km (382 mi), linking a number of lakes and rivers to provide a route from Gothenburg (Göteborg) on the west coast to Söderköping on the Baltic Sea via the river Göta älv and the Trollhätte kanal, through the large lakes Vänern and Vättern. More details
13. Kiel Canal:
The Kiel Canal is a 98-kilometre (61 mi) long freshwater canal in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. The canal was finished in 1895, but later widened, and links the North Sea at Brunsbüttel to the Baltic Sea at Kiel-Holtenau. An average of 250 nautical miles (460 km) is saved by using the Kiel Canal instead of going around the Jutland Peninsula. This not only saves time but also avoids storm-prone seas and having to pass through the Sound or Belts. More details
The Kiel Canal is a 98-kilometre (61 mi) long freshwater canal in the German state of Schleswig-Holstein. The canal was finished in 1895, but later widened, and links the North Sea at Brunsbüttel to the Baltic Sea at Kiel-Holtenau. An average of 250 nautical miles (460 km) is saved by using the Kiel Canal instead of going around the Jutland Peninsula. This not only saves time but also avoids storm-prone seas and having to pass through the Sound or Belts. More details
14. Welland Canal:
The Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, connecting Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. It forms a key section of the St. Lawrence Seaway. Traversing the Niagara Peninsula from Port Weller to Port Colborne, it enables ships to ascend and descend the Niagara Escarpment and bypass Niagara Falls. More details
The Welland Canal is a ship canal in Ontario, Canada, connecting Lake Ontario and Lake Erie. It forms a key section of the St. Lawrence Seaway. Traversing the Niagara Peninsula from Port Weller to Port Colborne, it enables ships to ascend and descend the Niagara Escarpment and bypass Niagara Falls. More details
15. Caledonian Canal:
The Caledonian Canal connects the Scottish east coast at Inverness with the west coast at Corpach near Fort William in Scotland. The canal was constructed in the early nineteenth century by Scottish engineer Thomas Telford, and is a sister canal of the Göta Canal in Sweden, also constructed by Telford. More details
The Caledonian Canal connects the Scottish east coast at Inverness with the west coast at Corpach near Fort William in Scotland. The canal was constructed in the early nineteenth century by Scottish engineer Thomas Telford, and is a sister canal of the Göta Canal in Sweden, also constructed by Telford. More details
16. Canals of Amsterdam:
Amsterdam, capital of the Netherlands, has more than one hundred kilometers of grachten (canals), about 90 islands and 1,500 bridges. The three main canals (Herengracht, Prinsengracht and Keizersgracht), dug in the 17th century during the Dutch Golden Age, form concentric belts around the city, known as the Grachtengordel. Alongside the main canals are 1550 monumental buildings. The 17th-century canal ring area, including the Prinsengracht, Keizersgracht, Herengracht and Jordaan, were listed as UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2010, contributing to Amsterdam's fame as the "Venice of the North". More details
Amsterdam, capital of the Netherlands, has more than one hundred kilometers of grachten (canals), about 90 islands and 1,500 bridges. The three main canals (Herengracht, Prinsengracht and Keizersgracht), dug in the 17th century during the Dutch Golden Age, form concentric belts around the city, known as the Grachtengordel. Alongside the main canals are 1550 monumental buildings. The 17th-century canal ring area, including the Prinsengracht, Keizersgracht, Herengracht and Jordaan, were listed as UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2010, contributing to Amsterdam's fame as the "Venice of the North". More details
17. Grand Canal of Ireland:
The Grand Canal is the southernmost of a pair of canals that connect Dublin, in the east of Ireland, with the River Shannon in the west, via Tullamore and a number of other villages and towns, the two canals nearly encircling Dublin's inner city. Its sister canal on the Northside of Dublin is the Royal Canal. The last working cargo barge passed through the Grand Canal in 1960. The idea of connecting Dublin to the Shannon was proposed as early as 1715, and in 1757 the Irish Parliament granted Thomas Omer £20,000 to start construction of a canal. By 1759 he reported that 3 km (1.9 mi) in the Bog of Allen and 13 km (8.1 mi) of canal from the River Liffey near Sallins towards Dublin were complete. More details
The Grand Canal is the southernmost of a pair of canals that connect Dublin, in the east of Ireland, with the River Shannon in the west, via Tullamore and a number of other villages and towns, the two canals nearly encircling Dublin's inner city. Its sister canal on the Northside of Dublin is the Royal Canal. The last working cargo barge passed through the Grand Canal in 1960. The idea of connecting Dublin to the Shannon was proposed as early as 1715, and in 1757 the Irish Parliament granted Thomas Omer £20,000 to start construction of a canal. By 1759 he reported that 3 km (1.9 mi) in the Bog of Allen and 13 km (8.1 mi) of canal from the River Liffey near Sallins towards Dublin were complete. More details
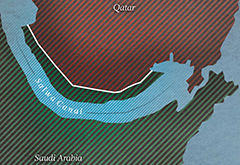
18. Salwa Canal:
The Salwa Canal is a proposed shipping route and tourism project through Saudi Arabia along its border with Qatar. In June 2017, Saudi Arabia along with several other countries cut diplomatic relations with Qatar and imposed a land, sea, and air blockade. The tender was scheduled to take place on 25 June 2018. According to the publication Makkah Al-Mukarramah, the company with the winning bid was to be announced within 90 days of the bid closure date, after which it was to begin digging of the channel immediately in order to complete the project within a one-year time frame. More details
The Salwa Canal is a proposed shipping route and tourism project through Saudi Arabia along its border with Qatar. In June 2017, Saudi Arabia along with several other countries cut diplomatic relations with Qatar and imposed a land, sea, and air blockade. The tender was scheduled to take place on 25 June 2018. According to the publication Makkah Al-Mukarramah, the company with the winning bid was to be announced within 90 days of the bid closure date, after which it was to begin digging of the channel immediately in order to complete the project within a one-year time frame. More details
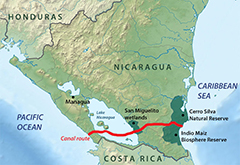
19. Nicaragua Canal:
The Nicaraguan Canal was a proposed shipping route through Nicaragua to connect the Caribbean Sea (and therefore the Atlantic Ocean) with the Pacific Ocean. Scientists were concerned about the project's environmental impact, as Lake Nicaragua is Central America's key freshwater reservoir while the project's viability was questioned by shipping experts and engineers. Construction of a canal using the San Juan River as an access route to Lake Nicaragua was first proposed in the early colonial era. The United States abandoned plans to construct a waterway in Nicaragua in the early 20th century after it purchased the French interests in the Panama Canal. More details
The Nicaraguan Canal was a proposed shipping route through Nicaragua to connect the Caribbean Sea (and therefore the Atlantic Ocean) with the Pacific Ocean. Scientists were concerned about the project's environmental impact, as Lake Nicaragua is Central America's key freshwater reservoir while the project's viability was questioned by shipping experts and engineers. Construction of a canal using the San Juan River as an access route to Lake Nicaragua was first proposed in the early colonial era. The United States abandoned plans to construct a waterway in Nicaragua in the early 20th century after it purchased the French interests in the Panama Canal. More details
20. Istanbul Canal:
The Istanbul Canal (Kanal İstanbul) is a project for the artificial sea-level waterway, which is planned by the Republic of Turkey on the European side of Turkey, connecting the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara, and thus to the Aegean and Mediterranean seas. Istanbul Canal would bisect the current European side of Istanbul and thus form an island between Asia and Europe (the island would have a shoreline with the Black Sea, Sea of Marmara, the new canal and the Bosporus). The new waterway would bypass the current Bosporus. Istanbul Canal aims to minimise shipping traffic in the Bosporus. It is projected to have a capacity of 160 vessel transits a day. More details
The Istanbul Canal (Kanal İstanbul) is a project for the artificial sea-level waterway, which is planned by the Republic of Turkey on the European side of Turkey, connecting the Black Sea to the Sea of Marmara, and thus to the Aegean and Mediterranean seas. Istanbul Canal would bisect the current European side of Istanbul and thus form an island between Asia and Europe (the island would have a shoreline with the Black Sea, Sea of Marmara, the new canal and the Bosporus). The new waterway would bypass the current Bosporus. Istanbul Canal aims to minimise shipping traffic in the Bosporus. It is projected to have a capacity of 160 vessel transits a day. More details